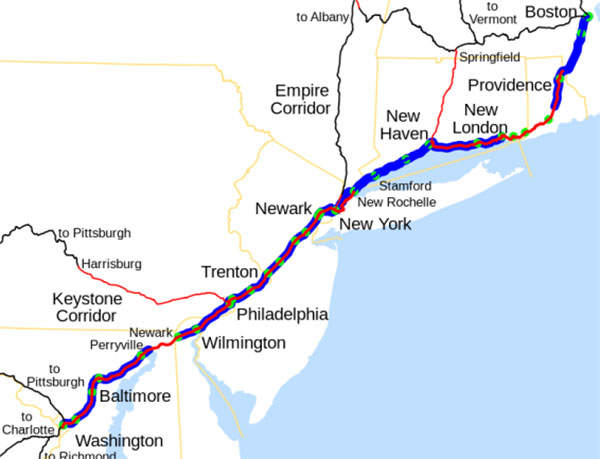
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is a 457-mile (735.5km) railway line connecting highly urbanised areas in the US. It is the busiest railroad in North America, stretching from the north to the south and passing through eight states. It starts from Boston, Massachusetts, and ends at Washington, DC, via New York, and linking several intermediate cities to the District of Columbia.
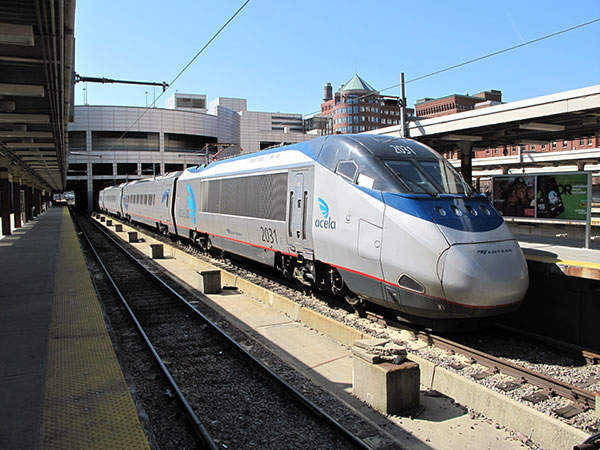
Operated by Amtrak, the fully electrified railway line carried 17.1 million passengers in FY2015. The Acela Express, a Northeast Regional service operating between New York and Washington, is run on the NEC. The corridor is also used by few other Amtrak routes, and various commuter and freight rail transport services.
In September 2010, Amtrak unveiled its plans to upgrade the NEC to a high-speed corridor operating at speeds of 220mph (354km/h). The upgrade is estimated to require a $151bn investment and is scheduled for completion by 2040.
The White House Council started a pilot programme to obtain Environmental Impact Review for the NEC high-speed rail project in January 2012. Construction started on a full scale in 2014.
History of the Northeast Corridor rail project and its upgrades
The NEC was built between 1830 and 1917, with electrification taking place between 1905 and 1938. Amtrak acquired the rights-of-way on the NEC in 1976 as the railroads operating the corridor had become bankrupt.
The Northeast Corridor Improvement Project (NECIP) started in 1976 to upgrade and modernise the line. It included safety improvements, modernisation of signalling systems, installation of new centralised electrification and traffic control (CETC) centres, and introduction of AEM-7 locomotives.
The Northeast High Speed Rail Improvement Program (NHRIP) was implemented on the line in 1990s. Acela Express trains were introduced to decrease travel times between cities. The grade crossings were eliminated, bridges were rebuilt, curves were modified and tracks were electrified to make them compatible with Acela trains.
The Acela Express train service on the NEC line started in December 2000. It marginally reduced the travel time between the cities, which allowed the train services to compete with airline services.
Related project
Illinois High Speed Rail Project, United States of America
The Illinois High Speed Rail (HSR) Project is a track development, implementation and operation programme to convert the existing 450km route between Chicago and St. Louis into a high speed rail service line.
Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor upgrade project details
The passenger traffic of the NEC eventually increased beyond its capacity with the introduction of Acela Express train service. Proposals for the upgrade of the NEC line were floated consequently. The Northeast Corridor Infrastructure Master Plan and A Vision for High Speed Rail in the Northeast Corridor were released in 2010.
Amtrak proposed a new high-speed corridor along the entire line, which provides for a new inland route through Connecticut. A brand new 426-mile double-track high-speed corridor was decided to be built, after a series of consultations and discussions. This new high-speed corridor will bring down travel times between Boston and Washington to approximately 3.5 hours.
The high-speed corridor will allow trains to run at 140mph (225km/h), whereas the current speed is just 75mph (120km/h), and all intermediate stations will be bypassed by means of tunnels and new stations. Amtrak expects the line to produce an annual profit of $1bn and increase the annual ridership to 38 million by 2050.
Development and construction of the high-speed Northeast Corridor
The NEC high-speed corridor is planned to be advanced under two programmes, the NEC Upgrade Program (NEC-UP) scheduled between 2012 and 2025, and the Next Generation High Speed Rail Program (NextGen HSR) for 2025 and 2040.
The NEC Capital Investment Program was formulated by key stakeholders of the NEC as a step towards realising the High Speed Up-Gradation Program.
The $14.7bn Gateway project was proposed by Amtrak in February 2011 and involves upgrades to the electrical, signalling and track infrastructure between Morrisville New Brunswick and New Jersey, which is one of the busiest segments of the NEC. Amtrak received $450m in funding towards the gateway project from the US Department of Transportation in May 2011.
The proposed project will be fully integrated with the new Northeast Corridor Infrastructure and Investment Development business line that was proposed in November 2011.
Contractors involved in Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor
Alstom received a $2bn contract from Amtrak for delivery of 28 high-speed trains for the Northeast Corridor in August 2016.
Alstom is also responsible for providing technical support, spare components and parts for the maintenance of the new trainsets.