Since 1975, Getzner from Bürs / Austria has been extremely successful in developing and producing foamed polyurethane elastomers. First the target was to realize reproducibility with the material Sylomer, then it was to develop this material for specific applications.
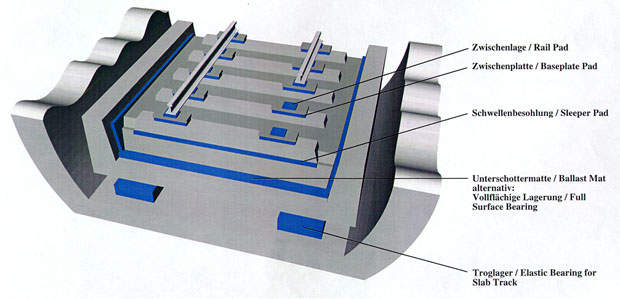
Now Getzner is characterized by individual elastic solutions within the segments track superstructure and the layering of buildings, machines and industry. The product range for track superstructure includes Sylomer® and Sylodyn® ballast mats, elastic resilient pads for rail fasteners and sleeper pads. Talking of systems, Getzner can already refer to international projects with its mass-spring-system and embedded-rail-system.
With more than 40 years’ experience in this sector, Getzner has amassed expertise in the field of elasticity of modern superstructures, which enables us to fulfil every specification in respect of elasticity, maintenance, noise and vibration for the international railway industry.
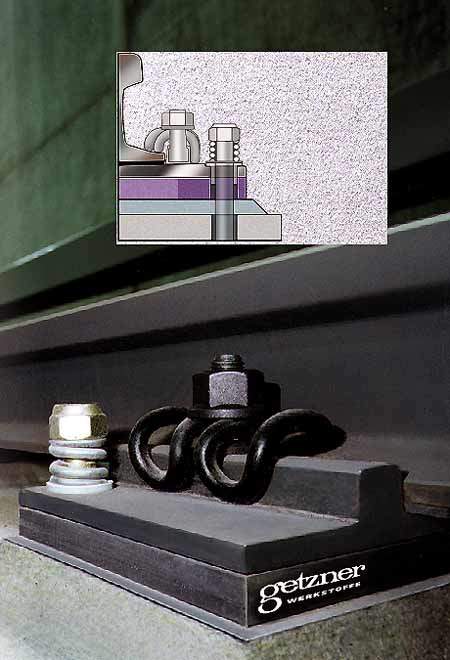
Rail and baseplate pads for resilient rail fasteners
Baseplate pads and rail pads produced by Getzner have been in use for more than 14 years as elastic components for rail fasteners.
Sylomer and Sylodyn baseplate pads and rail pads for elastic rail fasteners
Sylomer and Sylodyn resilient baseplate pads and rail pads are used on trams, subways, light rail and main lines for:
- Slab track elasticity
- Reduction of loads on the ballast
- Reduction of wheel-track interaction
- Reduction of secondary airborne noise from bridges
- Dampening of structure-borne noise
- Vibration damping for buildings
Elastic sleeper pads
Getzner sleeper pads are constructed of several layers. The isolation layer is firmly attached to the bottom of the sleeper and determines the elastic properties of the support. The load distribution layer is in direct contact with the ballast. This layer operates as mechanical protection for the insulation layer and distributes the forces over a wider area.
Applications for sleeper pads.
- Vibration isolation
- Increased track stability
- Adjustment of track stiffness
- Reduced rail corrugation
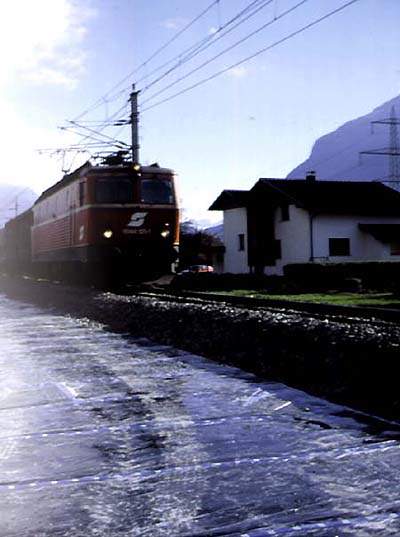
Sylomer and Sylodyn ballast mats
A complete range of ballast mats are available for subway, light rail and main line applications. Getzner ballast mats have been used as elastic bedding for ballasted railway track constructions since 1975.
The installation of ballast mats reduces the static and dynamic forces caused by rail traffic and transfers these forces evenly to the substructure.
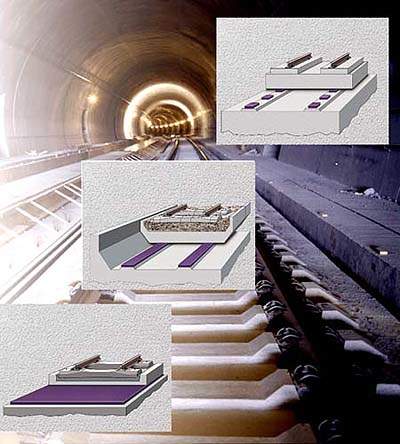
Elastic supports for slab tracks and ballast troughs – “mass-spring” systems
Sylomer and Sylodyn are ideal materials for elastic supports in all mass-spring systems.
A wide variety of measures are available for reducing structure-borne noise at the source. These measures include the use of highly elastic pads for rail fasteners, ballast mats, elastic supports for slab tracks and troughs, so-called “mass-spring systems”.
These mass-spring systems are used in applications where the isolation demands, in terms of structure-borne noise, are very high and where the use of these systems is possible.
Essentially, there are three different types of such systems:
- Full surface layer
- Linear support
- Discrete bearings
“Embedded rail” system
With its “embedded rail“ system, Getzner offers an attractive track solution that meets all the requirements. This system is highly attractive in terms of its long lifespan and cost-effectiveness, as well as its comfort and low noise generation.
Sylomer – a multi-faceted elastomer for track superstructures
For more than two decades now, Sylomer materials have been used in track superstructures as effective isolation against vibration and structure-borne noise. In this function, these materials also help to protect historical buildings, increase track stability and reduce the dynamic stresses on the ballast bed, thus keeping track maintenance costs low.
Sylodyn – the new generation of highly efficient elastomeric materials
Getzner has continued the development of the Sylomer materials that have been in use for many years and created a whole new generation of highly efficient polyurethane elastomers: Sylodyn. We offer a range of Sylodyn products that are designed specifically to meet the ever increasing dynamic stresses found in high performance rail operations: highly elastic inserts and pads, extremely effective ballast mats as well as supports for mass-spring systems.