HÜBNER is the leading global supplier of complete gangways and articulation systems for railway vehicles. Our long years of experience in manufacturing, construction and design have made us a reliable partner for vehicle manufacturers and transport authorities all over the world.
HÜBNER also develops many other system components for the transport vehicle industry, like vehicle parts made of PU-foam systems, moulded plastic and rubber parts, rubber profiles, window systems and easy entry ramps.
Bellows for railway vehicles
For more than 50 years HÜBNER has manufactured bellows for all kinds of railway vehicles, ranging from tramways to high-speed trains. We process high-quality materials from various fabrics with different elastomer and thermoplast coatings.
Depending on the usage and requirements the fabrics developed by us are provided with special properties, e.g. sound insulation, pressure stability, flexibility and increased flammability.
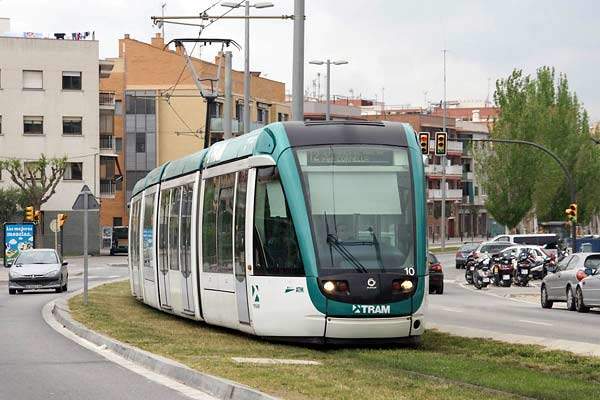
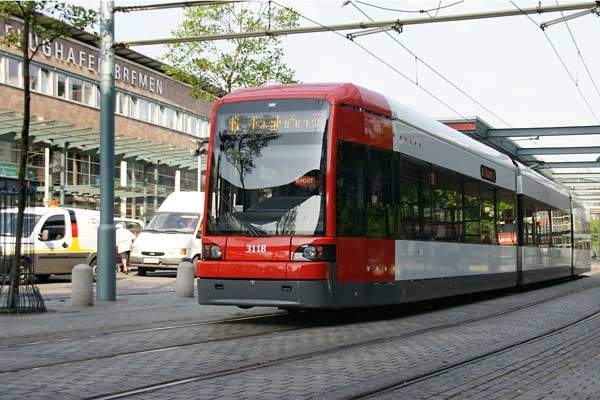
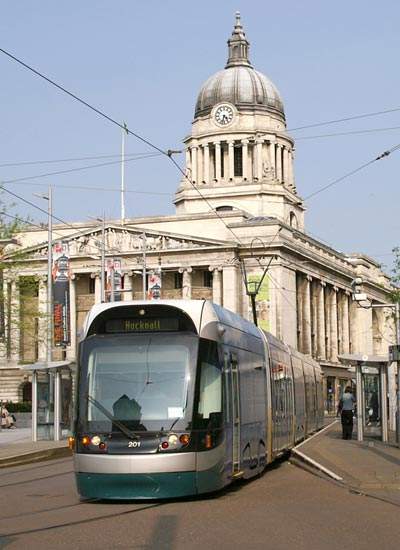
Gangways and articulation systems for light rail vehicles
Besides bellows, HÜBNER also offers complete gangway systems for tramways, including the necessary articulations. These gangways form the flexible part of the tram and absorb the movements of the individual wagon parts. This offers a safe and comfortable journey for the passengers plus an additional standing area in the tram. Due to its advantageous construction and careful material selection the gangway is virtually maintenance free and has a long service life.
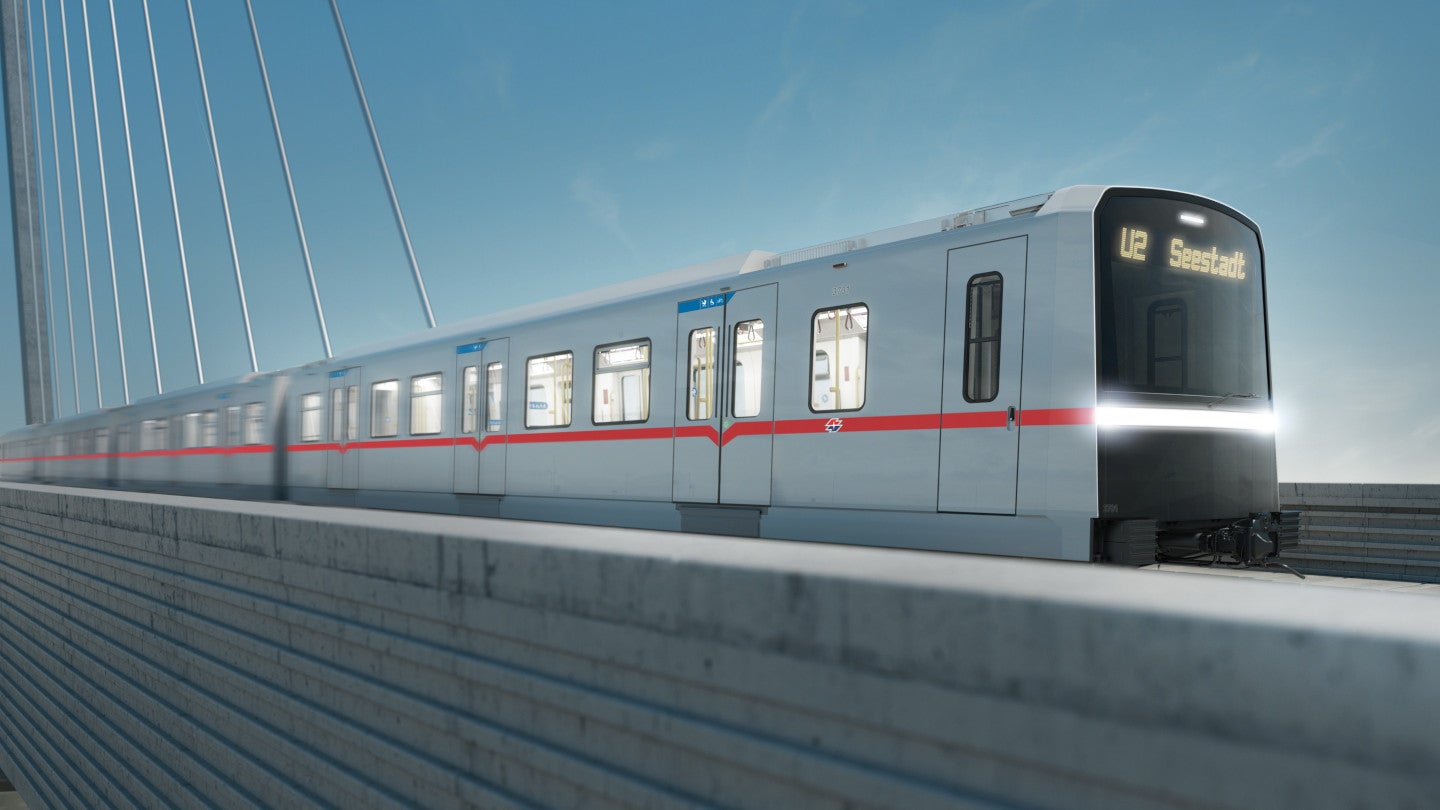
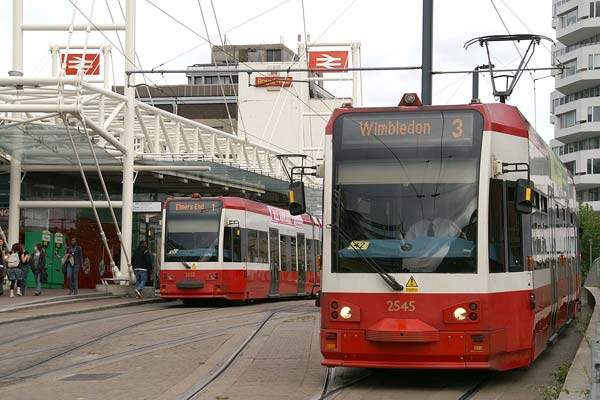
Comfort gangways for metros and commuter trains
The key requirements for metro and commuter train gangways include sound insulation, flammability and resistance to vandalism, as well as a large passage width and easy cleaning possibilities. With its gangway concept HÜBNER was able to fulfil those requirements (resulting from various specifications ranging from Europe to China) successfully on the international market.
The inner covering comprising the linking roof and the sidewalls, the bellows and the linking bridge form a flexible connection and a safe passageway between the wagons. Our practically vandalism-resistant inner coverings are not only adaptable to all kinds of railways due to their functional demands but also due to a wide choice of inner designs.
Gangways for regional trains
For rail vehicles in regional traffic HÜBNER offers a gangway concept that is individually adjustable to each type of vehicle. One or two-part gangways equipped with linking bridges or bridge plates are possible. Furthermore the gangways meet the requirements of wagon manufacturers and vehicle operators with regard to flammability, sound insulation, abrasion, tensile and bending force and buckling resistance.
Front end gangways
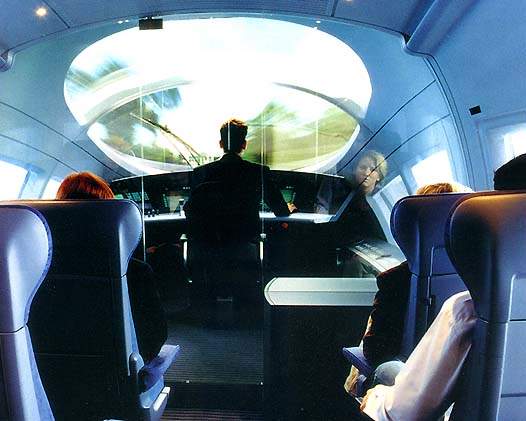
HÜBNER has developed several versions of front-end gangways, like the new modular front-end gangway, in which the halves can be torn back in the front of the vehicles and be closed by the outer doors. So the uncoupled vehicle receives a plain, tight, aesthetic and aero-dynamical front. The doors are secure against impact at a velocity of 400km/hr.
The complete gangway, including doors, will be built in the vehicle as a completely pre-mounted system. This extremely compact construction affords a comfortable broad gangway as well as enough space on both sides for the driver’s cabs.
Gangways for high-speed trains and long distance trains
These trains make special demands on compression stability, flexibility and flammability. On the basis of tests performed in our motion rack, as well as in our company-owned laboratory, we have achieved a high degree of efficiency and reliability for these special kind of gangways, with extraordinary detail to materials and safety. These comfortable gangways can be supplied in one or two
parts and are equipped with double bellows and a patented linking bridge.