Kazan Metro is a rapid transit system serving Kazan, the capital city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. Kazan is located 800km from Moscow and has a population of 1.5 million.
The first phase of Kazan Metro was opened on 27 August 2005 to commemorate the millennium anniversary of the city. Operated by MetroElektroTrans, it has a daily ridership of approximately 220,000 passengers. In 2011, 23.7 million passengers used the Kazan Metro.
Kazan Metro history
Plans for a rapid transit system in Kazan were proposed during the days of the Russian empire but shelved due to the October Revolution and Russian Civil war. During this period, Kazan was the capital of Tatar ASSR. The city was then a rapidly developing business and industrial centre.
In 1935, implementation of the Moscow Metro provided the much-needed impetus for the construction of a rapid transit system in Kazan. Proposals for the metro, however, were postponed again due to World War II.
In late 1970s, Kazan’s population crossed the one million mark, calling for an intercity transport system, and planning for the metro system restarted in 1983. Feasibility and environmental impact studies were carried out in 1984 and planning for the first stage of the project was submitted to government authorities. The Soviet Union broke up in 1991, making it difficult to source funds for the project.
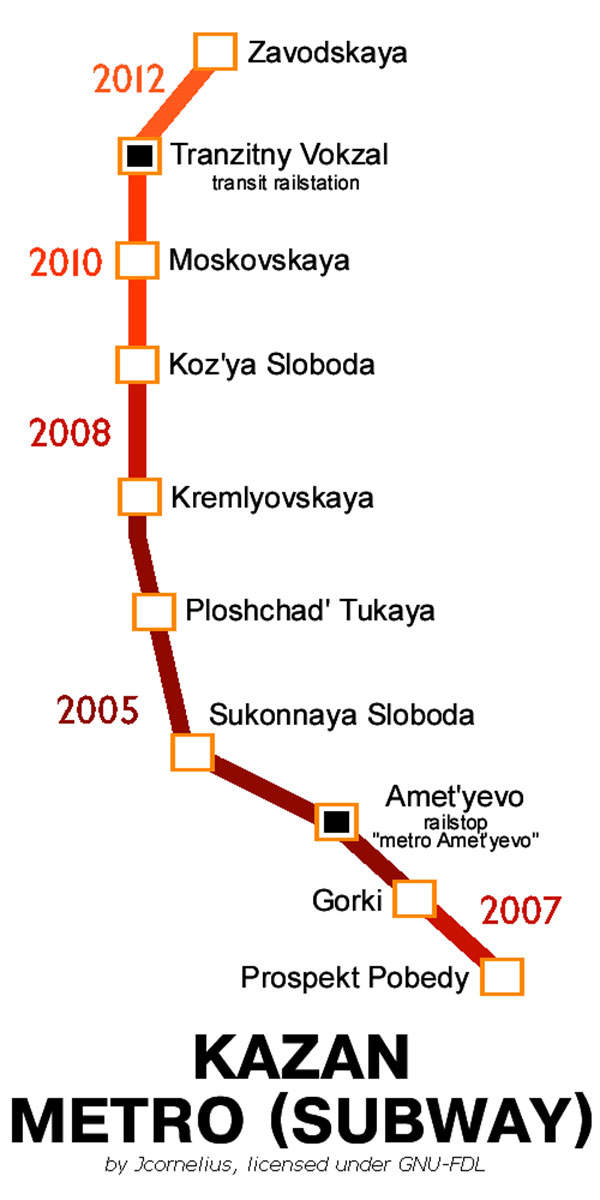
Due to the growing economy of Kazan, the Federal government issued an order to review the project in 1995. The project was restarted and a ground-breaking ceremony was held on 27 August 1997. 2005 was fixed as the deadline for completion, which also marked the millennium anniversary of Kazan.
Project details of Kazan Metro
The first stage of Kazan Metro included five stations, constructed in deep-level tunnels. The pace of construction in the initial stages was relatively slow due to a lack of financial support, however the Russian Ministry of Transport brought in metro brigades from Samara and Moscow to increase the pace.
Construction of a difficult path that runs under the Kazanka River was continuously postponed and the Almaty Metro construction brigade from Kazakhstan was brought in to help with the action.
Related project
Moscow Metro, Russian Federation
The Moscow Metro is one of the world’s busiest underground railway systems, and also one of the most extensive. However, the network is now under severe strain as nine million passengers use the 298.2km system every day, and there is an urgent need to reduce the amount of passengers at city centre interchanges, and on the current ring line.
By the end of 2004, eight boring crew were employed for the construction of 13 tunnels and the metro line was inaugurated as per the schedule in August 2005.
Two more lines from Vokzal to Azino and Volga to Savinovo are planned for completion in phases from 2013 to 2021.
Construction of underground tunnels between the Hills and Victory Avenue stations were completed in March 2007. Two tunnel boring systems namely Olga and Pauline were used for the excavation work. The extension of the line to Prospekt Pobedy, which is located south of Gorki station, was completed in December 2008.
The tunnel beneath the Kazanka River was completed in 2009, while a new station, Gates Quarter, was unveiled in December 2010. Completion of the entire line is scheduled for May 2013, with three new stations, Moskovskaya, Severny Vokzal and Sotsgorod, set to be opened. All tunnel work between Kozia Sloboda to Sotsgorod was completed by July 2012. As of 2012 the metro line is 10.9km long with seven stations.
Kazan Metro infrastructure
The Kazan metro’s infrastructure is one of the most modern systems among all Russian metros. The whole line runs on a 1524mm broad gauge track.
The metro’s control system was developed at the St. Petersburg NII Scientific Research Institute and designed by Iconics UK. It completely eliminated the use of obsolete relays that were previously used. The current control suite is capable of determining the conditions across the line and monitoring train movement, station equipment conditions, railway track conditions, duplicated optical channels and reservation data, ensuring safety and comfort for passengers.
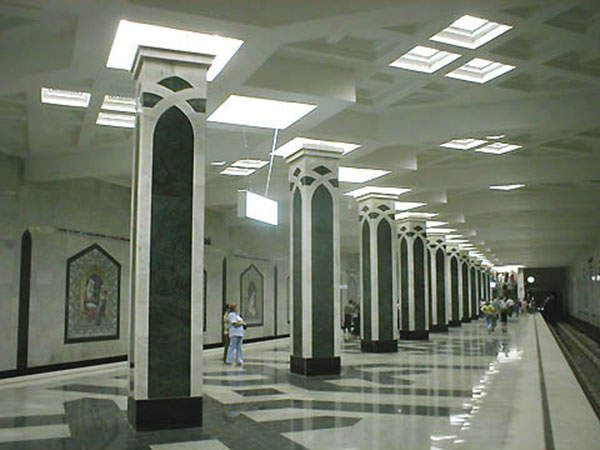
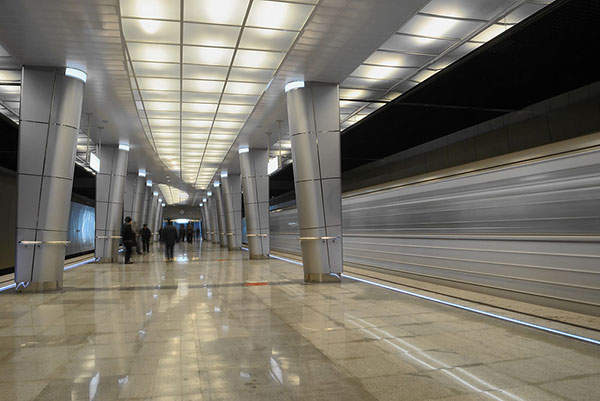
Each Kazan Metro station has its own architectural theme. Two stations are currently single-vault, two are pillar-spans and one exists on a blended glass glazed flyover.
Kazan Metro offers smart-tokens, with travel validity for one day, and smartcards, which are valid for several trips or a fixed length of time. MOBATIME supplied the time displays used in the stations.
Kazan Metro rolling stock
The rolling stock for operation on Kazan Metro was designed by Vagonmash in co-operation with Škoda Dopravní Technika of Plzeň, Czech Republic. UniControls designed the traction drive units.
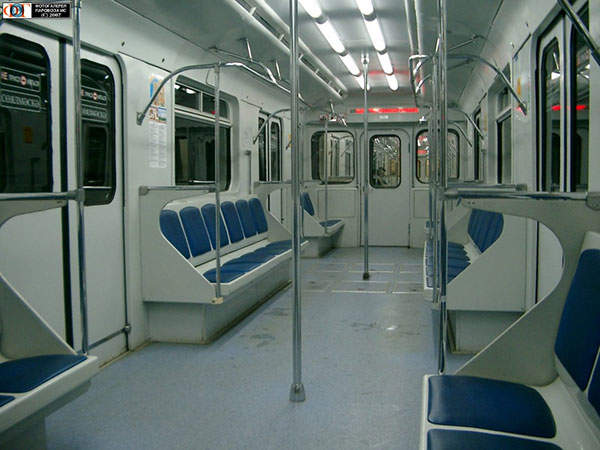
The metro uses two types of cars 81-553.3 (head) and 81-554.3 (standard) and each train has four cars. The 81-553.3 model can accommodate 310 passengers, whereas the 81-554.3 has a capacity for 370 passengers. The trains are fully automated and capable of operating without an onboard engineer and driver.
A new set of five three-car trains named Rusich was also bought for the metro. Repair and maintenance of the rolling stock is carried out at the Daurskoye depot.
The future of Kazan Metro
There are proposals to extend Kazan Metro to five lines by 2030 and create a light urban railway system. The plan is to build a circular line consisting of two sections, and three radial lines.